
The silicone creates an indent, which pushes the eye-wall back onto the retina.

See your doctor or eye specialist straightaway if you experience any of the above visual disturbances, because a retinal detachment needs prompt corrective surgery to prevent permanent damage to your eyesight. A retinal tear may be accompanied by the sensation of flashing lights in the affected eye or showers of dark floaters and blurred vision.Īs the retina detaches it often causes a dark shadow, like a curtain or veil, in the peripheral vision, which usually progresses to complete vision loss. Anyone who has had a severe eye injury.People who have undergone cataract surgery.People at increased risk of retinal detachment include: Injury to the eye can also cause retinal detachment, although this is less common. Once such a tear or hole develops, fluid can collect beneath it and reduce the adhesion of the retina to the choroid, resulting in a detachment. The most common cause of retinal detachment is age-related shrinkage of the vitreous gel, which may lead to tearing at a weak point in the retina. When the retina is detached it can no longer function and vision is lost.
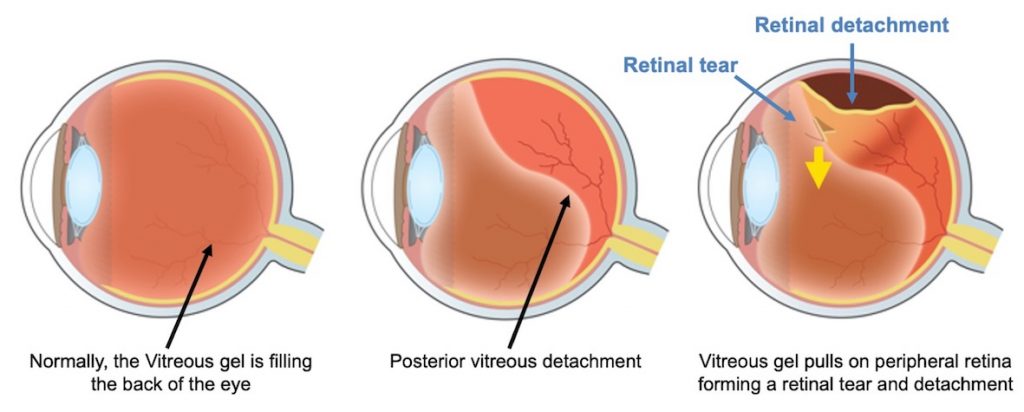
Retinal detachment is when the retina pulls away from the tissue around it (the choroid), which supplies it with oxygen and nutrients. Nerve fibres leaving the retina bundle together to form the optic nerve, which relays visual information to the brain. On its outer side the retina is attached to the choroid, or middle layer, which is rich in blood vessels. It is supported on the inside by the jelly-like vitreous, which fills the eyeball behind the lens.
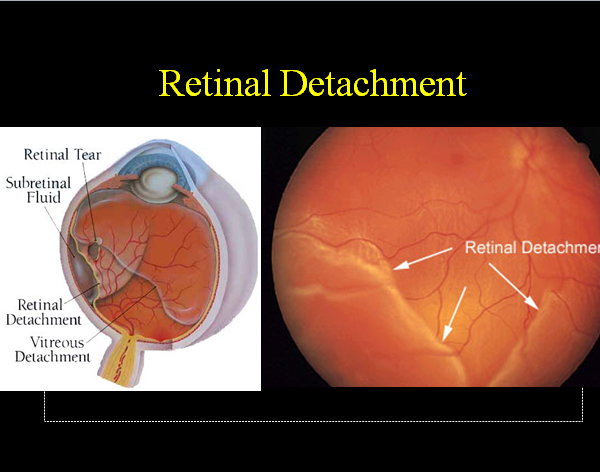
The retina is the innermost layer of the wall of the eye and is made up of light sensitive cells known as rods and cones, which detect shape, colour and pattern.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
